Thermal Transfer VS Direct Thermal:
Direct thermal label printing has traditionally been a niche technology used across several narrow vertical markets including meat, poultry and dairy. However, developments in thermal paper technology have resulted in a broader range of products that are now suitable for use in many applications across nearly any vertical market. The result has been increased interest in direct thermal as the technology choice for new or upgraded applications.
Five Key Considerations

(3) THERMAL PRINTHEAD LIFE & COST
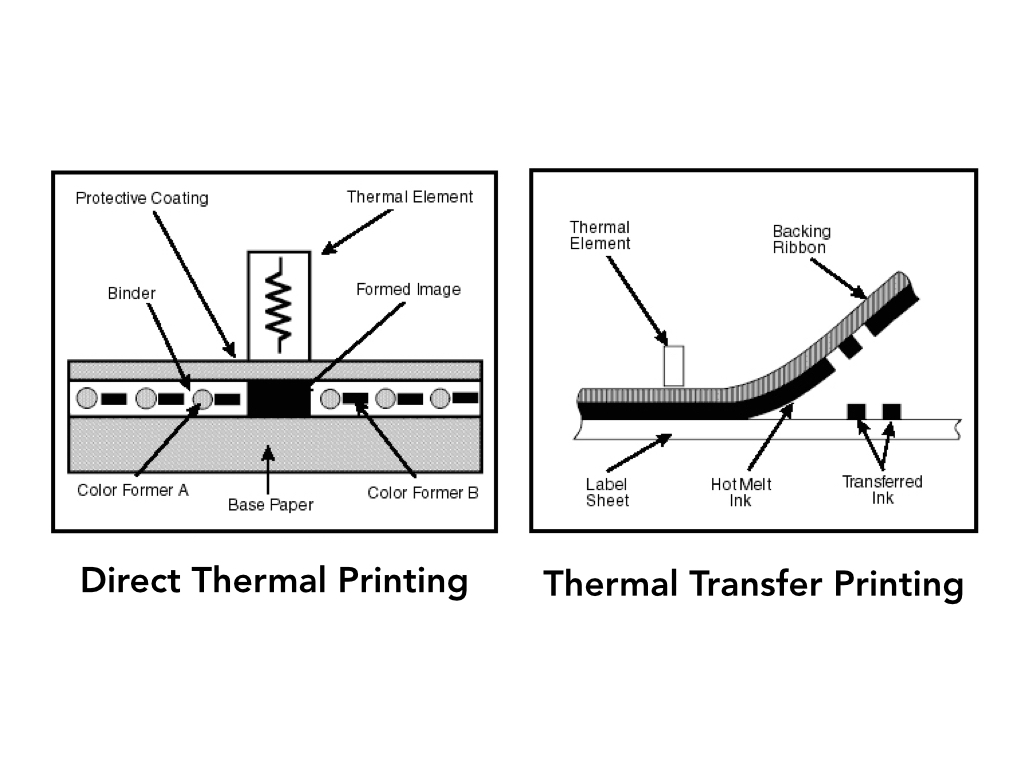
From the above comparison, note that direct thermal printing requires the printhead elements be in direct contact with the label material as it is pulled across the printhead. Conversely, thermal transfer printing has thermal ribbon acting as a “buffer” between the printhead elements and the label material. Generally speaking, a company should anticipate direct thermal printheads providing an expected lifetime of 25% – 50% of a thermal transfer printhead.
(4) MEDIA SELECTION & COST
The specific type of direct thermal media used is often the least considered aspect of most evaluations, but likely the most important. Not only will a company’s media choice directly impact the cost of labels, it will also impact the life of the printhead, upper-end print speed capabilities and print quality. These are important considerations as they may impact the ongoing cost of operations.
(5) ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS
In today’s world of reduced carbon footprints, waste reduction and sustainability, environmental considerations have become crucial for many organizations. Waste reduction and lower carbon footprints are increasingly part of corporate mission statements and, in some cases, used to increase competitive advantage.
(1) PRINTER CONFIGURATION & COST
Printer configuration is one area where some cost savings will be available. Thermal transfer printers normally have the capability of printing either thermal transfer or direct thermal. These printers are generally less costly to purchase because they do not contain any of the hardware necessary for driving and controlling ribbon.
(2) LABEL LIFE REQUIREMENTS
Requirements surrounding label life get back to the heart of the difference between direct thermal labels and thermal transfer labels. Direct thermal printed labels simply do not offer the same lifetime as a thermal transfer printed label. An organization must know its label life requirements before considering direct thermal labels.

Advantages & Disadvantages for Thermal Transfer and Direct Thermal
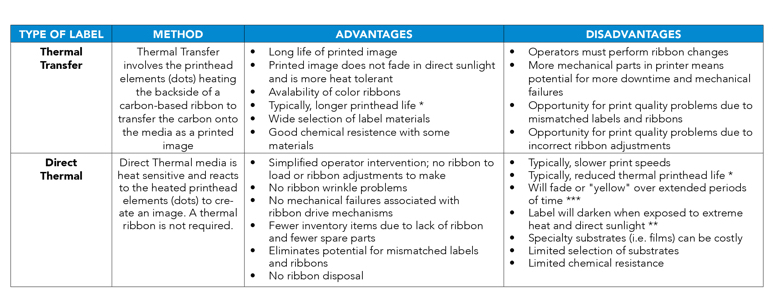
* When using the Pakar Recetak M8459Se direct thermal print engine or the M5900RVe direct thermal printer, the specific printhead used in these models has an expected printhead life that compares favorably to thermal transfer printheads.
*** Pakar Rekacetak offers patented direct thermal materials that are more resistant to abrasion, direct sunlight, UV light and chemical contamination than traditional direct thermal media.
